As electric vehicles dominate the automotive market, the spotlight shifts to their safety records. The Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning are two of the most anticipated models in the electric truck segment, but how do they stack up when it comes to crash safety? The latest results from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) provide essential insights into their performance under rigorous testing circumstances.
In this article, we will delve into the Tesla Cybertruck vs Ford F-150 Lightning crash test results, highlighting key findings such as frontal crash performance, child seat anchor usability, and headlight ratings. We will also discuss the implications of these results for potential buyers looking for safety without compromising on innovation and technology. Buckle up as we explore the nuances of safety in these remarkable electric trucks!
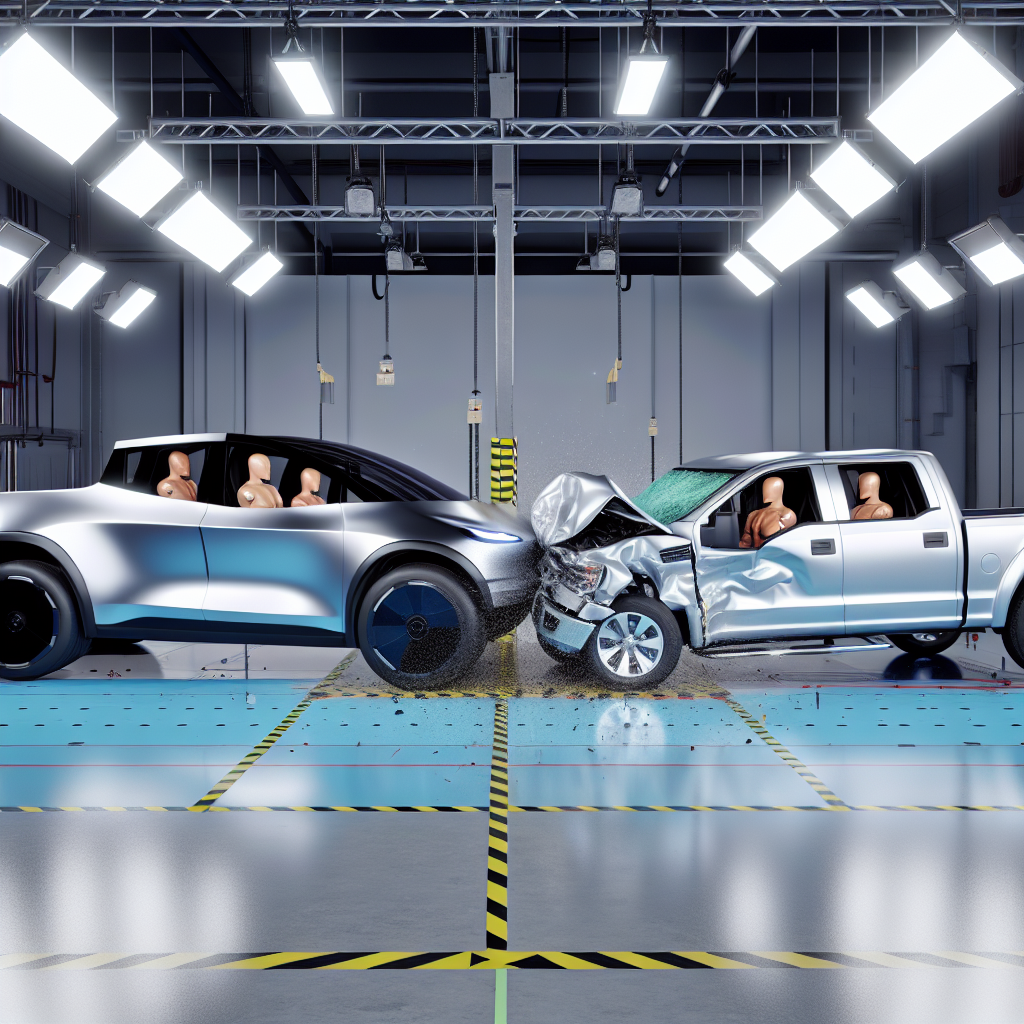

Comparison of Crash Test Results
The Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning have undergone various safety evaluations, including frontal crash tests, rear-seat safety assessments, and headlight performance reviews. Below is a comparison based on available data:
Frontal Crash Tests:
- Tesla Cybertruck: The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) awarded the Cybertruck a five-star overall safety rating. In frontal crash tests simulating a head-on collision at 35 mph, the driver received a five-star rating, while the front passenger received four stars. Notably, the knee airbags did not deploy during this test, which Tesla stated was by design for this specific configuration.
- Ford F-150 Lightning: NHTSA’s frontal crash tests for the F-150 Lightning resulted in four-star ratings for both the driver and front passenger.
Rear-Seat Safety:
- Tesla Cybertruck: In the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety’s (IIHS) moderate overlap front crash test, the Cybertruck achieved a “Good” rating. This test evaluates the vehicle’s performance in a collision where 40% of the front end collides with a barrier at 40 mph.
- Ford F-150 Lightning: The F-150 Lightning received a “Marginal” rating in the same IIHS test. Measurements from the rear dummy indicated a high risk of chest, head, or neck injuries. Additionally, the rear dummy’s lap belt shifted from the pelvis to the abdomen, increasing the risk of internal injuries.
Headlight Performance:
- Tesla Cybertruck: IIHS rated the Cybertruck’s headlights as “Poor,” citing excessive glare from the low beams as a significant issue.
- Ford F-150 Lightning: The F-150 Lightning’s headlights received an “Acceptable” rating from IIHS, indicating better performance compared to the Cybertruck.
In summary, while both vehicles have demonstrated strong safety features, the Tesla Cybertruck generally outperforms the Ford F-150 Lightning in frontal crash tests and rear-seat safety assessments. However, the F-150 Lightning has superior headlight performance.
Crash Test Ratings Comparison Table
The following table compares the crash test ratings of the Tesla Cybertruck and the Ford F-150 Lightning across various categories:
-
Frontal Crash Rating:
- Tesla Cybertruck: 5 stars for driver, 4 stars for passenger
- Ford F-150 Lightning: 4 stars for both driver and passenger
-
Rear-Seat Dummy Safety:
- Tesla Cybertruck: Good
- Ford F-150 Lightning: Marginal
-
Headlight Performance:
- Tesla Cybertruck: Poor
- Ford F-150 Lightning: Acceptable
This comparison highlights key differences in safety performance between the two electric vehicles, making it easier for consumers to assess their choices based on reliable crash test ratings.
IIHS Methodologies
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) uses several strict testing methods to assess how well vehicles, like the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning, can withstand crashes. These methods help consumers understand vehicle safety ratings that influence their buying choices. The IIHS conducts various tests to evaluate different aspects of vehicle safety, each designed to imitate real-world crash situations.
- Moderate Overlap Front Test: This test mimics a head-on collision where 40% of the vehicle’s front strikes a barrier at 40 mph. It measures the vehicle’s structure and the effectiveness of safety features like airbags and seatbelts. Higher ratings in this category mean better protection for occupants in frontal crashes.
- Side Impact Test: This test evaluates how well vehicles protect occupants in side collisions. It checks how much the passenger compartment intrudes and how effective side curtain airbags are.
- Roof Strength Test: This test measures how well a vehicle’s roof can hold up in a rollover accident. A strong roof design can help protect passengers in rollovers, leading to higher safety scores.
- Rear Crash Tests: This test looks at the safety of rear-seat passengers and evaluates how well head restraints and seat designs prevent whiplash injuries during rear-end collisions.
- Headlight Performance Evaluations: The IIHS also tests headlight performance, focusing on road illumination and glare reduction for other drivers. This aspect is crucial for safe night driving.
The IIHS rates vehicles as “Good,” “Acceptable,” “Marginal,” or “Poor.” These ratings give consumers a clear picture of a vehicle’s safety features. They are important because they heavily influence consumer choices, insurance rates, and manufacturer designs. High ratings show a commitment to safety, while lower ratings may push manufacturers to improve vehicle safety.
By understanding the IIHS methodologies, consumers can make better choices when evaluating the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning, helping to contribute to safer roads for everyone.
Insights from IIHS Findings
The findings from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) reveal a compelling narrative about the safety performance of the Tesla Cybertruck and the Ford F-150 Lightning, each leading the charge in electric vehicle innovation. The IIHS praised the Cybertruck by stating, “For models built after April 2025, the Cybertruck showcases a remarkable ‘Good’ rating in the moderate overlap front crash test, reflecting a commitment to occupant protection that is commendable in today’s automotive landscape.” This ratings distinction fails to overshadow the concerning aspect of its headlight performance, which was noted as “Poor” due to excessive glare, making night driving potentially hazardous for both occupants and other road users.
Conversely, the IIHS raised concerns about the Ford F-150 Lightning, which earned a “Poor” rating in the same crash test. Their assessment highlighted that while the Lightning provided good protection for the driver, “the rear-seat occupants faced an alarming risk of severe chest, head, and neck injuries due to the rear dummy’s lap belt shifting to the abdomen, thereby increasing the likelihood of internal harm.” This analysis underscores the critical importance of rear-seat safety, which cannot be overshadowed in vehicles that are often used to transport families.
Through these insightful findings, the IIHS prompts potential buyers to prioritize safety by stating, “Comprehensive safety evaluations are essential, particularly for vehicles designed for family transporters. The Tesla Cybertruck, with its superior ratings in frontal crash performance, sets a new standard, while the Ford F-150 Lightning must address critical safety vulnerabilities to remain competitive in the ever-evolving electric vehicle market.” Their assessment not only elevates safety awareness but also calls for manufacturers to push for continuous improvements in design and engineering.
In conclusion, as consumers navigate the choices in the electric truck market, these findings shed light on the varying protective capacities of these two vehicles. With critical ratings shaping the purchasing landscape, cars like the Cybertruck can lead the industry towards safer designs that benefit all occupants.
Conclusion
In closing, the safety test results for the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning provide invaluable insights for consumers in the electric vehicle market. The findings from the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) clearly illustrate significant advantages in safety features for both vehicles, yet substantial differences remain. The Tesla Cybertruck has consistently outperformed the Ford F-150 Lightning in frontal crash tests, achieving commendable scores that reflect a strong commitment to occupant protection. Notably, the Cybertruck’s child seat anchor usability also garnered praise, reinforcing the vehicle’s suitability for families.
In contrast, the Ford F-150 Lightning, while praised for its overall design and performance, struggled in the area of rear-seat safety and received a poor rating for rear-seat dummy safety, raising concerns about the potential risk to passengers.
Safety remains an overarching priority in the evolving landscape of electric vehicles, and these test results highlight the responsibility consumers have in making informed decisions. As electric trucks make their way into more households, understanding these safety ratings is imperative to ensure the well-being of all occupants.
As you evaluate your options in the electric vehicle market, consider these crash test findings seriously. The safety features of the vehicles you choose not only impact your driving experience but also the lives of your loved ones. By selecting vehicles like the Tesla Cybertruck with proven safety ratings, you are investing in a future of safer, more responsible transportation. Choose wisely and drive safely!
Implications of Safety Ratings
The impact of crash test ratings extends beyond the assessments conducted by institutions like the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). For consumers, safety ratings are crucial factors influencing buying decisions. When faced with high-stakes choices regarding vehicle acquisitions, buyers naturally lean towards models that demonstrate superior safety records. The growing consumer awareness about vehicle safety has led to an increased demand for detailed safety performance data, making crash test ratings not just numbers, but pivotal influences on purchase behavior.
A vehicle with outstanding safety ratings often garners trust from potential buyers, as these ratings signal years of engineering diligence and commitment to occupant protection. For instance, the favorable evaluations that the Tesla Cybertruck received allow it to stand out among competitors. With safety being a top priority for families, consumers are more likely to consider vehicles that are well-rated in crash safety, which translates to increased sales and market share for manufacturers who prioritize these developments.
Conversely, poor safety ratings present significant challenges for manufacturers. A low rating can adversely affect a vehicle’s reputation, leading to reduced consumer confidence and diminished sales. Automotive companies must grapple with the implications not just from a marketing perspective but also in terms of liability and insurance costs. Vehicles that do not meet safety expectations can experience higher insurance premiums or even legal repercussions should safety concerns lead to accidents or injuries.
Furthermore, the responsibilities of manufacturers extend beyond merely achieving high safety ratings. They have an ethical obligation to leverage crash test results to innovate designs and enhance safety features continually. When a vehicle falls short in certain areas—such as rear-seat safety in the Ford F-150 Lightning—it should motivate manufacturers to not only address these issues in future models but also to offer potential retrofits or solutions for existing vehicles. Manufacturers must be proactive rather than reactive to consumer feedback driven by safety test outcomes.
The implications of safety ratings go far beyond mere statistics; they encapsulate a broader narrative of trust, innovation, and consumer responsibility. As electric vehicles, such as the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning, gain traction in the automotive market, the focus on safety will remain a critical component shaping brand loyalty and consumer choices. Consequently, both buyers and manufacturers must pay close attention to safety performance evaluations, ensuring that the vehicles they support and invest in align with the highest safety standards available.

As of September 2025, user adoption data indicates that the Ford F-150 Lightning is leading in registrations compared to the Tesla Cybertruck. According to S&P Global Mobility data, during the first quarter of 2025, the F-150 Lightning achieved 7,913 registrations, surpassing the Cybertruck’s 7,126 registrations. Notably, in March 2025, the Lightning had 2,598 registrations, exceeding the Cybertruck’s 2,170. This trend illustrates a clear preference for the F-150 Lightning among early adopters of electric trucks.
Several factors contribute to this adoption rate. The F-150 Lightning appeals to traditional truck buyers thanks to its design, which aligns closely with conventional pickup aesthetics, and its competitive starting price of $65,190 for a well-equipped all-wheel-drive model. In contrast, the Cybertruck features a more futuristic design coupled with a higher initial price point of $71,985 for the base rear-wheel-drive version, possibly limiting its broader market appeal.
Regarding safety features, while specific statistical insights from user feedback are scarce, there are significant safety concerns for the Cybertruck. In March 2025, a recall affected 46,096 units due to an exterior panel issue, and by mid-May, the NHTSA reported that the Cybertruck was associated with eight recalls. These incidents have likely influenced consumer perceptions about the safety and reliability of the Cybertruck.
On the other hand, the F-150 Lightning has not faced similar recalls or safety concerns during this time period, which may further enhance its adoption rates and positive feedback regarding its safety features.
In summary, while both electric trucks have made impressive strides in the market, the F-150 Lightning’s traditional design, competitive pricing, absence of major recalls, and overall brand loyalty contribute significantly to its higher user adoption rates compared to the Tesla Cybertruck.
IIHS Methodologies
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS) uses several strict testing methods to assess how well vehicles, like the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning, can withstand crashes. These methods help consumers understand vehicle safety ratings that influence their buying choices. The IIHS conducts various tests to evaluate different aspects of vehicle safety, each designed to imitate real-world crash situations.
- Moderate Overlap Front Test: This test mimics a head-on collision where 40% of the vehicle’s front strikes a barrier at 40 mph. It measures the vehicle’s structure and the effectiveness of safety features like airbags and seatbelts. Higher ratings in this category mean better protection for occupants in frontal crashes. More details can be found on the IIHS Testing Methods.
- Side Impact Test: This test evaluates how well vehicles protect occupants in side collisions. It checks how much the passenger compartment intrudes and how effective side curtain airbags are. Learn more at IIHS Side Impact Testing.
- Roof Strength Test: This test measures how well a vehicle’s roof can hold up in a rollover accident. A strong roof design can help protect passengers in rollovers, leading to higher safety scores. Additional information is available at IIHS Roof Strength Tests.
- Rear Crash Tests: This test looks at the safety of rear-seat passengers and evaluates how well head restraints and seat designs prevent whiplash injuries during rear-end collisions. More on this test can be accessed through IIHS Rear Crash Testing.
- Headlight Performance Evaluations: The IIHS also tests headlight performance, focusing on road illumination and glare reduction for other drivers. This aspect is crucial for safe night driving. Find further details at IIHS Headlight Assessment.
The IIHS rates vehicles as “Good,” “Acceptable,” “Marginal,” or “Poor.” These ratings give consumers a clear picture of a vehicle’s safety features. They are important because they heavily influence consumer choices, insurance rates, and manufacturer designs. High ratings show a commitment to safety, while lower ratings may push manufacturers to improve vehicle safety.
By understanding the IIHS methodologies, consumers can make better choices when evaluating the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning, helping to contribute to safer roads for everyone.
Implications of Safety Ratings
The impact of crash test ratings extends beyond the assessments conducted by institutions like the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS). For consumers, safety ratings are crucial factors influencing buying decisions. When faced with high-stakes choices regarding vehicle acquisitions, buyers naturally lean towards models that demonstrate superior safety records. The growing consumer awareness about vehicle safety has led to an increased demand for detailed safety performance data, making crash test ratings not just numbers, but pivotal influences on purchase behavior.
A vehicle with outstanding safety ratings often garners trust from potential buyers, as these ratings signal years of engineering diligence and commitment to occupant protection. For instance, the favorable evaluations that the Tesla Cybertruck received allow it to stand out among competitors. With safety being a top priority for families, consumers are more likely to consider vehicles that are well-rated in crash safety, which translates to increased sales and market share for manufacturers who prioritize these developments.
Conversely, poor safety ratings present significant challenges for manufacturers. A low rating can adversely affect a vehicle’s reputation, leading to reduced consumer confidence and diminished sales. Automotive companies must grapple with the implications not just from a marketing perspective but also in terms of liability and insurance costs. Vehicles that do not meet safety expectations can experience higher insurance premiums or even legal repercussions should safety concerns lead to accidents or injuries.
Furthermore, the responsibilities of manufacturers extend beyond merely achieving high safety ratings. They have an ethical obligation to leverage crash test results to innovate designs and enhance safety features continually. When a vehicle falls short in certain areas—such as rear-seat safety in the Ford F-150 Lightning—it should motivate manufacturers to not only address these issues in future models but also to offer potential retrofits or solutions for existing vehicles. Manufacturers must be proactive rather than reactive to consumer feedback driven by safety test outcomes.
The implications of safety ratings go far beyond mere statistics; they encapsulate a broader narrative of trust, innovation, and consumer responsibility. As electric vehicles, such as the Tesla Cybertruck and Ford F-150 Lightning, gain traction in the automotive market, the focus on safety will remain a critical component shaping brand loyalty and consumer choices. Consequently, both buyers and manufacturers must pay close attention to safety performance evaluations, ensuring that the vehicles they support and invest in align with the highest safety standards available.
Crash Test Ratings Comparison Table
The following table summarizes the crash test ratings of the Tesla Cybertruck and the Ford F-150 Lightning, showcasing their performance across multiple important safety categories:
| Safety Category | Tesla Cybertruck | Ford F-150 Lightning |
|---|---|---|
| Frontal Crash Rating | 5 stars (Driver), 4 stars (Passenger) | 4 stars (Driver and Passenger) |
| Rear-Seat Dummy Safety | Good | Marginal |
| Headlight Performance | Poor | Acceptable |
This visual summary allows consumers to easily compare the safety ratings of these electric trucks, making informed choices when considering their next vehicle purchase.