As the beating heart of commerce, the trucking industry is currently navigating one of its most tumultuous periods in decades. Rising fuel costs, crippling supply chain disruptions, and a labor shortage have combined to create a perfect storm that threatens the very fabric of this vital sector. In response, federal measures designed to alleviate some of these burdens have sparked intense debate among industry stakeholders.
The Canadian Trucking Alliance (CTA) has raised alarms, cautioning that while these relief measures may offer short-term benefits, they might also inadvertently reward practices like misclassification and tax evasion, further complicating the landscape. “After more than five years of effort to attract attention to this important issue, the industry is counting on the Government of Canada to do the right thing and to end the abuse in Canada’s trucking sector,” stated Stephen Laskowski, President of the CTA, highlighting the critical need for careful consideration of these policies.
As discussions around federal interventions ramp up, the stakes have never been higher for the trucking industry and its contributors, making it imperative for all voices to be heard before any decisions are made.
Federal Measures Impacting the Trucking Industry
In 2023, the Canadian federal government introduced several key measures aimed at addressing various challenges facing the trucking industry while promoting safety, sustainability, and fair labor practices. Here’s an overview of these federal initiatives along with the intended benefits and criticisms that have emerged from industry leaders:
-
Mandatory Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs)
Starting January 2023, the use of Electronic Logging Devices has become mandatory for drivers to monitor their Hours of Service (HOS). This regulation aims to combat driver fatigue and enhance road safety. However, industry insiders have voiced concerns that this could create logistic challenges, particularly for livestock transportation during peak seasons.
-
Crackdown on Driver Misclassification
The government allocated a significant budget of $26.3 million over five years to combat the ongoing issue of driver misclassification under the “Driver Inc.” model, where drivers are labeled as independent contractors to avoid offering benefits. Critics argue that this practice creates an uneven playing field, hampering compliant companies’ competitiveness. Alain Bédard from TFI International emphasized the need for fairness and compliance in addressing these disparities.
-
Carbon Tax Implementation
The introduction of a carbon tax applied to diesel fuel seeks to incentivize a shift toward greener fuel alternatives. However, the Canadian Trucking Alliance (CTA) has contested this measure, asserting that the alternative fuels suitable for long-haul trucking are not yet available or feasible. The anticipated economic impact is projected to add nearly $2 billion to trucking costs by 2024, leading to potential price rises for consumers without immediate environmental benefits.
-
Investments in Workforce Development
In response to a persistent labor shortage, up to $46.3 million has been allocated to support Trucking Human Resources Canada. This investment aims to enhance the recruitment, training, and retention of new drivers. While well-intended, industry leaders are cautious about the efficacy of these measures to genuinely address the workforce requirements in the sector.
-
Addressing Interprovincial Trade Barriers
The federal government has recognized that regulatory discrepancies between provinces can hinder trucking operations. A recent report indicated that removing these interprovincial trade barriers could add over $1.6 billion to Canada’s GDP annually. Advocates within the industry are promoting mutual recognition agreements to unify regulations and streamline operations across provinces.
Overall, while these federal measures are designed to create a safer, more equitable, and environmentally friendly trucking industry, they have also ignited debates regarding the practicality of implementation, financial implications, and the readiness of the industry to adapt to these sweeping changes.
Economic Challenges in the Trucking Industry
The trucking industry is currently beset by a trio of formidable economic challenges: rising fuel costs, labor shortages, and increasing regulatory pressures. These factors are significantly affecting operational efficiency and the bottom line for many carriers.
Rising Fuel Costs
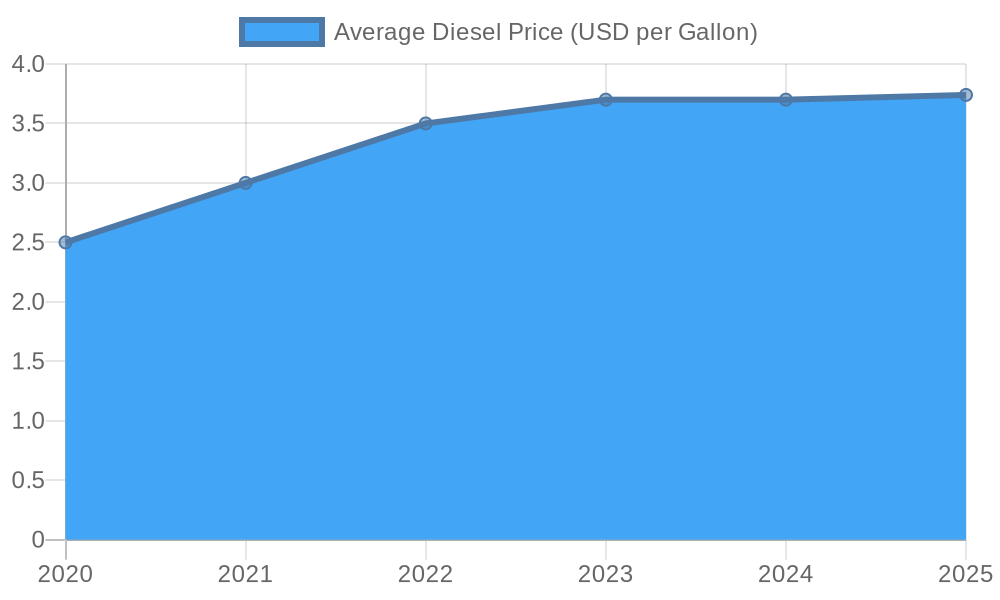
Fuel expenses have become a pressing concern for trucking companies, particularly as diesel prices have seen significant increases. According to a survey conducted in July 2025, over half of U.S. transport and shipping companies allocate 20% or more of their monthly operating budgets to fuel costs due to soaring diesel prices. This financial strain complicates investments in technologies designed to lower costs in the long run, such as route optimization software and fuel-efficient vehicles. This trend not only squeezes existing budgets but also limits innovation in a sector where efficiency is paramount.
Labor Shortages
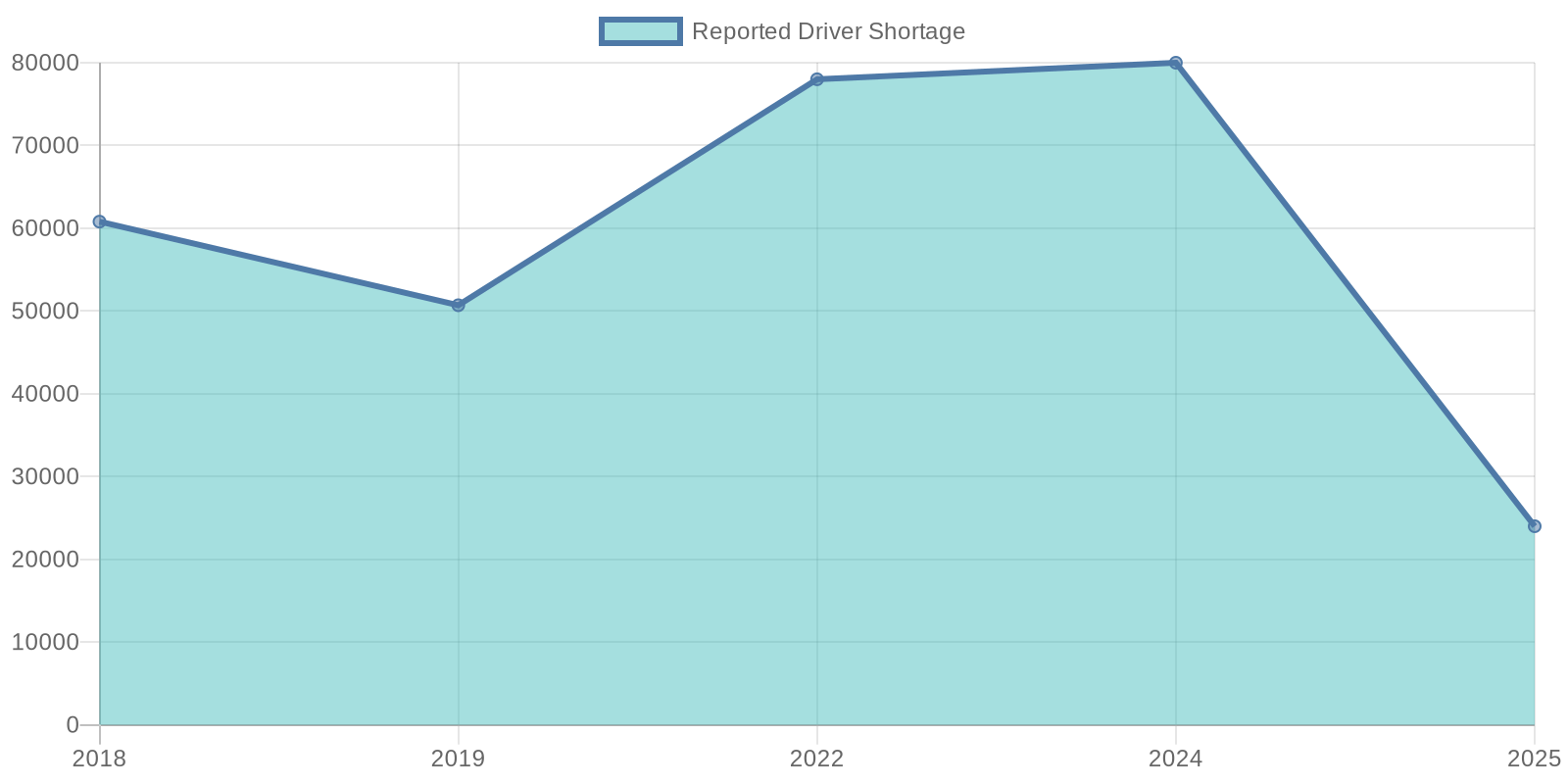
Labor shortages have created a further challenge for the trucking industry. The American Trucking Associations has estimated a shortage of over 78,000 drivers, a figure that is expected to grow as the workforce ages and younger generations seek employment in other sectors. The turnover rate for large carriers exceeds 90%, significantly impacting productivity and service reliability. Factors contributing to this labor crisis include long hours, challenging working conditions, and stagnant wages, which discourage new drivers from joining the industry. These persistent shortages mean that many companies are operating at less than full capacity, leading to delays and increased operational costs.
Increasing Regulatory Pressures
The trucking industry also faces mounting regulatory pressures as compliance requirements evolve. Stricter environmental regulations, including emission standards, are introducing additional costs for carriers. Proposed mandates requiring safety devices such as speed limiters and automatic emergency braking systems threaten to further burden companies, adding to the complexity of operations and potentially delaying deliveries. Industry stakeholders argue that while regulations aim to enhance safety and sustainability, they can also hinder operational flexibility and profitability.
Conclusion
These economic challenges have collectively squeezed profit margins in the trucking industry. For example, truckload carriers reported an average operating margin of -2.3% in 2024, a decline from 3% in 2023 and 8% in 2022. This persistent trend of rising costs coupled with operational challenges calls for the trucking sector to adopt strategic investments and reforms to stabilize profitability while adapting to an increasingly complex economic landscape.
Addressing these issues is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability and efficiency of the trucking industry, requiring coordinated efforts among industry leaders, policymakers, and stakeholders.
| Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Short-term financial relief for carriers | Increased risk of rule-breaking and non-compliance |
| Support for workforce recruitment and training | Potential for misclassification of drivers |
| Incentives to adopt more environmentally friendly practices | Economic burden on carriers due to compliance costs |
| Enhanced operational efficiency through streamlined regulations | Risk of some companies exploiting loopholes |
| Improved safety standards through regulations | Possible delays in operations as new measures are implemented |

An illustration of modern trucking operations, showing trucks on a busy highway and personnel interacting.

An illustration highlighting challenges in the trucking industry, featuring fuel prices, labor shortages, and regulatory pressures.
Rule-Breaking Risks in the Trucking Industry
As the trucking industry grapples with novel challenges, the introduction of federal relief measures aimed at providing support can sometimes incite unintended consequences, particularly concerning rule-breaking behaviors such as misclassification and tax evasion. These risks pose significant concerns not only for the integrity of the industry but also for compliant carriers and the broader economy.
Misclassification of Workers
One of the primary risks associated with federal relief measures is the potential for increased misclassification of drivers. Misclassification typically occurs when drivers are incorrectly labeled as independent contractors instead of employees. This practice allows companies to circumvent responsibilities tied to employee benefits and labor rights, creating an uneven playing field where compliant businesses are left at a competitive disadvantage. This misclassification issue has been consistently highlighted by advocates for fair labor practices, including the Canadian Trucking Alliance, which noted that misclassification undermines efforts to ensure compliance and promote worker rights.
Tax Evasion Concerns
In tandem with misclassification, federal relief measures could inadvertently encourage tax evasion among trucking companies. With financial pressures mounting, some carriers may be tempted to exploit loopholes in tax regulations, impacting revenue streams crucial for public services. This behavior not only erodes the financial footing of legitimate businesses but also undermines economic stability industry-wide. The ramifications of widespread tax evasion can ripple across the economy, leading to budget deficits and reduced funding for critical infrastructure projects.
Compounding Economic Pressures
The intersection of misclassification and tax evasion is further exacerbated by the existing economic challenges within the trucking sector. With rising fuel costs, labor shortages, and increasing operational expenses due to regulatory changes, carriers face a precarious financial landscape. The allure of short-term gains offered by federal aid might tempt companies to adopt unethical practices, ultimately compromising their long-term viability and contributing to a cycle of instability within the industry.
Impact on Compliant Carriers
For carriers striving to adhere to regulations and maintain ethical business practices, the risks posed by those engaging in rule-breaking can be particularly disheartening. These compliant carriers often find themselves competing against companies that benefit from unfair advantages gained through misclassification and tax evasion. This creates an environment where ethical operations are undermined, and it hampers the overall progress toward fostering a reliable and transparent trucking industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while federal relief measures may be well-meaning attempts to stabilize the trucking industry amid economic turmoil, they carry inherent risks that could lead to increased misclassification and tax evasion among carriers. Addressing these issues is crucial to uphold fair labor standards and maintain a level playing field. Stakeholders within the industry, including policymakers, must tread carefully as they consider the implications of these measures to ensure that they do not inadvertently reward rule-breaking at the expense of ethical and compliant operations.
Conclusion
The trucking industry stands at a pivotal juncture, grappling with significant economic challenges that include skyrocketing fuel costs, critical labor shortages, and increasing regulatory pressures. Together, these factors have strained profit margins, with truckload carriers experiencing an average operating margin decline. As federal measures are introduced to mitigate some of these hurdles, it is essential for industry stakeholders to approach these changes with a discerning perspective.
Key Takeaways:
- Economic Challenges: Rising fuel costs, significant labor shortages, and rigorous regulations threaten the operational efficiency and profitability of trucking companies.
- Federal Measures Introduced: Initiatives such as mandatory Electronic Logging Devices, crackdowns on driver misclassification, workforce development investments, and carbon tax implementations signify the government’s attempt to enhance the sector’s safety, compliance, and environmental stewardship.
- Caution Against Unintended Consequences: There are genuine concerns regarding the potential for certain measures to inadvertently reward unethical practices like misclassification and tax evasion.
Recommendations:
- Foster Collaboration: Industry leaders, policymakers, and workers need to collaborate proactively. Sharing best practices and strategies can enhance compliance and promote ethical operations.
- Educate Stakeholders: Companies must prioritize educating their teams regarding compliance with federal measures, ensuring that all employees understand their rights and responsibilities.
- Maintain Vigilance: Stakeholders should remain vigilant against economic pressures that may encourage unethical practices. This includes employing robust internal controls to mitigate the risks of misclassification and tax evasion.
- Invest in Innovation: To combat rising operational costs, the industry must adopt innovative technologies that enhance efficiency. Investments in automation and route optimization can significantly reduce fuel expenditures in the long run.
In summation, while challenges abound, the trucking industry has the potential to emerge stronger from this period of uncertainty. By focusing on compliance, ethical practices, and collaboration, stakeholders can navigate economic difficulties and ensure a more sustainable future, ultimately fostering a resilient trucking ecosystem that adheres to fair labor standards and operational integrity.
The path forward requires careful consideration and a collective effort to align federal measures with the reality of industry operations, thereby safeguarding the interests of all players involved.
User Adoption Data Regarding Federal Relief Measures in the Trucking Industry
In recent years, the trucking industry has seen a notable response to federal relief measures designed to alleviate challenges like driver shortages, labor retention, and operational efficiencies.
Here’s a summary of key data and trends related to how trucking companies have adopted these measures:
Adoption of Federal Relief Measures
- Trucking Action Plan (TAP): The U.S. Departments of Transportation and Labor launched the TAP to create new pathways into the trucking profession, including expanding high-quality training through Registered Apprenticeship programs.
Over 100 employers, including notable companies like Domino’s, Frito-Lay, and UPS, have adopted these programs, collectively adding over 10,000 apprenticeships in the workforce. [source]
Trends and Key Statistics
- Employment Growth: Following the implementation of TAP, the trucking industry experienced significant employment growth, marking the best three-month period for long-distance trucking hiring since the 1990s.
Real wages for frontline truckers have also shown an upward trajectory despite inflation concerns. [source]
- Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) Issuance: Streamlined processes for issuing CDLs have resulted in over 876,000 new licenses being issued since January 2021, more than doubling new issuances in early 2022 compared to the same time period in 2021.
Overall Impacts on the Industry
- Addressing Driver Shortages: The American Trucking Associations (ATA) has indicated a severe driver shortage, estimating over 80,000 in 2021 and projections of exceeding 160,000 by 2030 without intervention.
Federal initiatives like TAP are essential to address this issue by enhancing job quality and retention efforts. [source]
- Economic Contributions: In 2020, trucking accounted for 10.23 billion tons of freight movement and generated $732.3 billion in revenue.
The sector continues to be the dominant mode of freight transport, representing 80.4% of the nation’s freight bill. [source]
In conclusion, trucking companies are responding actively to federal relief measures, showcasing substantial employment growth, increasing the number of CDL holders, and addressing critical driver shortages while reinforcing the trucking industry’s vital contribution to the economy.
As the beating heart of commerce, the trucking industry is currently navigating one of its most tumultuous periods in decades. Rising fuel costs, crippling supply chain disruptions, and persistent labor shortages represent some of the major trucking industry challenges that threaten the very fabric of this vital sector. In response, federal relief measures designed to alleviate some of these burdens have sparked intense debate among industry stakeholders. The Canadian Trucking Alliance (CTA) has raised alarms, cautioning that while these relief measures may offer short-term benefits, they might also inadvertently reward practices like misclassification and tax evasion, further complicating the landscape. “After more than five years of effort to attract attention to this important issue, the industry is counting on the Government of Canada to do the right thing and to end the abuse in Canada’s trucking sector,” stated Stephen Laskowski, President of the CTA, highlighting the critical need for careful consideration of these policies. As discussions around federal interventions ramp up, the stakes have never been higher for the trucking industry and its contributors, making it imperative for all voices to be heard before any decisions are made.
Federal Measures Impacting the Trucking Industry
In 2023, the Canadian federal government introduced several key measures aimed at addressing various trucking industry challenges, including truck driver shortages, while promoting safety, sustainability, and fair labor practices. Here’s an overview of these federal initiatives along with the intended benefits and criticisms that have emerged from industry leaders:
1. Mandatory Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs)
Starting January 2023, the use of Electronic Logging Devices has become mandatory for drivers to monitor their Hours of Service (HOS). This regulation aims to combat driver fatigue and enhance road safety. However, industry insiders have voiced concerns that this could create logistic challenges, particularly for livestock transportation during peak seasons.
2. Crackdown on Driver Misclassification
The government allocated a significant budget of $26.3 million over five years to combat the ongoing issue of driver misclassification under the “Driver Inc.” model, where drivers are labeled as independent contractors to avoid offering benefits. Critics argue that this practice creates an uneven playing field, hampering compliant companies’ competitiveness. Alain Bédard from TFI International emphasized the need for fairness and compliance in addressing these disparities.
3. Carbon Tax Implementation
The introduction of a carbon tax applied to diesel fuel seeks to incentivize a shift toward greener fuel alternatives. However, the Canadian Trucking Alliance (CTA) has contested this measure, asserting that the alternative fuels suitable for long-haul trucking are not yet available or feasible. The anticipated economic impact is projected to add nearly $2 billion to trucking costs by 2024, leading to potential price rises for consumers without immediate environmental benefits.
4. Investments in Workforce Development
In response to a persistent labor shortage, up to $46.3 million has been allocated to support Trucking Human Resources Canada. This investment aims to enhance the recruitment, training, and retention of new drivers. While well-intended, industry leaders are cautious about the efficacy of these measures to genuinely address the workforce requirements in the sector.
5. Addressing Interprovincial Trade Barriers
The federal government has recognized that regulatory discrepancies between provinces can hinder trucking operations. A recent report indicated that removing these interprovincial trade barriers could add over $1.6 billion to Canada’s GDP annually. Advocates within the industry are promoting mutual recognition agreements to unify regulations and streamline operations across provinces.
Overall, while these federal measures are designed to create a safer, more equitable, and environmentally friendly trucking industry, they have also ignited debates regarding the practicality of implementation, financial implications, and the readiness of the industry to adapt to these sweeping changes.
Economic Challenges in the Trucking Industry
The trucking industry is currently beset by a trio of formidable economic challenges: rising fuel costs, truck driver shortages, and increasing regulatory pressures. These factors are significantly affecting operational efficiency and the bottom line for many carriers.
Rising Fuel Costs
Fuel expenses have become a pressing concern for trucking companies, particularly as diesel prices have seen significant increases. According to a survey conducted in July 2025, over half of U.S. transport and shipping companies allocate 20% or more of their monthly operating budgets to fuel costs due to soaring diesel prices. This financial strain complicates investments in technologies designed to lower costs in the long run, such as route optimization software and fuel-efficient vehicles. This trend not only squeezes existing budgets but also limits innovation in a sector where efficiency is paramount.
Labor Shortages
Labor shortages have created a further challenge for the trucking industry. The American Trucking Associations has estimated a shortage of over 78,000 drivers, a figure that is expected to grow as the workforce ages and younger generations seek employment in other sectors. The turnover rate for large carriers exceeds 90%, significantly impacting productivity and service reliability. Factors contributing to this labor crisis include long hours, challenging working conditions, and stagnant wages, which discourage new drivers from joining the industry. These persistent shortages mean that many companies are operating at less than full capacity, leading to delays and increased operational costs.
Increasing Regulatory Pressures
The trucking industry also faces mounting regulatory pressures as compliance requirements evolve. Stricter environmental regulations, including emission standards, are introducing additional costs for carriers. Proposed mandates requiring safety devices such as speed limiters and automatic emergency braking systems threaten to further burden companies, adding to the complexity of operations and potentially delaying deliveries. Industry stakeholders argue that while regulations aim to enhance safety and sustainability, they can also hinder operational flexibility and profitability.
Conclusion
These economic challenges have collectively squeezed profit margins in the trucking industry. For example, truckload carriers reported an average operating margin of -2.3% in 2024, a decline from 3% in 2023 and 8% in 2022. This persistent trend of rising costs coupled with operational challenges calls for the trucking sector to adopt strategic investments and reforms to stabilize profitability while adapting to an increasingly complex economic landscape.
Addressing these issues is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability and efficiency of the trucking industry, requiring coordinated efforts among industry leaders, policymakers, and stakeholders.
| Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|
| Short-term financial relief for carriers | Increased risk of rule-breaking and non-compliance |
| Support for workforce recruitment and training | Potential for misclassification of drivers |
| Incentives to adopt more environmentally friendly practices | Economic burden on carriers due to compliance costs |
| Enhanced operational efficiency through streamlined regulations | Risk of some companies exploiting loopholes |
| Improved safety standards through regulations | Possible delays in operations as new measures are implemented |

An illustration of modern trucking operations, showing trucks on a busy highway and personnel interacting.

An illustration highlighting challenges in the trucking industry, featuring fuel prices, labor shortages, and regulatory pressures.
Rule-Breaking Risks in the Trucking Industry
As the trucking industry grapples with novel challenges, the introduction of federal relief measures aimed at providing support can sometimes incite unintended consequences, particularly concerning rule-breaking behaviors such as misclassification and tax evasion. These risks pose significant concerns not only for the integrity of the industry but also for compliant carriers and the broader economy.
Misclassification of Workers
One of the primary risks associated with federal relief measures is the potential for increased misclassification of drivers. Misclassification typically occurs when drivers are incorrectly labeled as independent contractors instead of employees. This practice allows companies to circumvent responsibilities tied to employee benefits and labor rights, creating an uneven playing field where compliant businesses are left at a competitive disadvantage. This misclassification issue has been consistently highlighted by advocates for fair labor practices, including the Canadian Trucking Alliance, which noted that misclassification undermines efforts to ensure compliance and promote worker rights.
Tax Evasion Concerns
In tandem with misclassification, federal relief measures could inadvertently encourage tax evasion among trucking companies. With financial pressures mounting, some carriers may be tempted to exploit loopholes in tax regulations, impacting revenue streams crucial for public services. This behavior not only erodes the financial footing of legitimate businesses but also undermines economic stability industry-wide. The ramifications of widespread tax evasion can ripple across the economy, leading to budget deficits and reduced funding for critical infrastructure projects.
Compounding Economic Pressures
The intersection of misclassification and tax evasion is further exacerbated by the existing economic challenges within the trucking sector. With rising fuel costs, labor shortages, and increasing operational expenses due to regulatory changes, carriers face a precarious financial landscape. The allure of short-term gains offered by federal aid might tempt companies to adopt unethical practices, ultimately compromising their long-term viability and contributing to a cycle of instability within the industry.
Impact on Compliant Carriers
For carriers striving to adhere to regulations and maintain ethical business practices, the risks posed by those engaging in rule-breaking can be particularly disheartening. These compliant carriers often find themselves competing against companies that benefit from unfair advantages gained through misclassification and tax evasion. This creates an environment where ethical operations are undermined, and it hampers the overall progress toward fostering a reliable and transparent trucking industry.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while federal relief measures may be well-meaning attempts to stabilize the trucking industry amid economic turmoil, they carry inherent risks that could lead to increased misclassification and tax evasion among carriers. Addressing these issues is crucial to uphold fair labor standards and maintain a level playing field. Stakeholders within the industry, including policymakers, must tread carefully as they consider the implications of these measures to ensure that they do not inadvertently reward rule-breaking at the expense of ethical and compliant operations.
Conclusion
The trucking industry stands at a pivotal juncture, grappling with significant economic challenges that include skyrocketing fuel costs, critical labor shortages, and increasing regulatory pressures. Together, these factors have strained profit margins, with truckload carriers experiencing an average operating margin decline. As federal measures are introduced to mitigate some of these hurdles, it is essential for industry stakeholders to approach these changes with a discerning perspective.
Key Takeaways:
- Economic Challenges: Rising fuel costs, significant labor shortages, and rigorous regulations threaten the operational efficiency and profitability of trucking companies.
- Federal Measures Introduced: Initiatives such as mandatory Electronic Logging Devices, crackdowns on driver misclassification, workforce development investments, and carbon tax implementations signify the government’s attempt to enhance the sector’s safety, compliance, and environmental stewardship.
- Caution Against Unintended Consequences: There are genuine concerns regarding the potential for certain measures to inadvertently reward unethical practices like misclassification and tax evasion.
Recommendations:
- Foster Collaboration: Industry leaders, policymakers, and workers need to collaborate proactively. Sharing best practices and strategies can enhance compliance and promote ethical operations.
- Educate Stakeholders: Companies must prioritize educating their teams regarding compliance with federal measures, ensuring that all employees understand their rights and responsibilities.
- Maintain Vigilance: Stakeholders should remain vigilant against economic pressures that may encourage unethical practices. This includes employing robust internal controls to mitigate the risks of misclassification and tax evasion.
- Invest in Innovation: To combat rising operational costs, the industry must adopt innovative technologies that enhance efficiency. Investments in automation and route optimization can significantly reduce fuel expenditures in the long run.
In summation, while challenges abound, the trucking industry has the potential to emerge stronger from this period of uncertainty. By focusing on compliance, ethical practices, and collaboration, stakeholders can navigate economic difficulties and ensure a more sustainable future, ultimately fostering a resilient trucking ecosystem that adheres to fair labor standards and operational integrity.
The path forward requires careful consideration and a collective effort to align federal measures with the reality of industry operations, thereby safeguarding the interests of all players involved.
User Adoption Data Regarding Federal Relief Measures in the Trucking Industry
In recent years, the trucking industry has seen a notable response to federal relief measures designed to alleviate challenges like driver shortages, labor retention, and operational efficiencies. Here’s a summary of key data and trends related to how trucking companies have adopted these measures:
Adoption of Federal Relief Measures
- Trucking Action Plan (TAP): The U.S. Departments of Transportation and Labor launched the TAP to create new pathways into the trucking profession, including expanding high-quality training through Registered Apprenticeship programs. Over 100 employers, including notable companies like Domino’s, Frito-Lay, and UPS, have adopted these programs, collectively adding over 10,000 apprenticeships in the workforce. (source)
Trends and Key Statistics
- Employment Growth: Following the implementation of TAP, the trucking industry experienced significant employment growth, marking the best three-month period for long-distance trucking hiring since the 1990s. Real wages for frontline truckers have also shown an upward trajectory despite inflation concerns. (source)
- Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) Issuance: Streamlined processes for issuing CDLs have resulted in over 876,000 new licenses being issued since January 2021, more than doubling new issuances in early 2022 compared to the same time period in 2021. (source)
Overall Impacts on the Industry
- Addressing Driver Shortages: The American Trucking Associations (ATA) has indicated a severe driver shortage, estimating over 80,000 in 2021 and projections of exceeding 160,000 by 2030 without intervention. Federal initiatives like TAP are essential to address this issue by enhancing job quality and retention efforts. (source)
- Economic Contributions: In 2020, trucking accounted for 10.23 billion tons of freight movement and generated $732.3 billion in revenue. The sector continues to be the dominant mode of freight transport, representing 80.4% of the nation’s freight bill. (source)
In conclusion, trucking companies are responding actively to federal relief measures, showcasing substantial employment growth, increasing the number of CDL holders, and addressing critical driver shortages while reinforcing the trucking industry’s vital contribution to the economy.


